**主讲 李金鹏 北汽新能源数据库负责人 **

Statement Level:基于SQL语句复制的,只会讲SQL语句记录到binlog中。这种模式只存储SQL,没有真正的数据,所以无法数据恢复,生产环境一般也不会用这种模式
Row Level:基于行的复制,并且会将每一条的数据变化记录到日志文件中,是没有SQL语句的。这种我们可以解析出真正的数据,生产中建议采用。缺点就是记录时产生大量的binlog,面对存储过程时可能出现数据不一致的情况。
Mixed:混合的一种模式,默认情况下是Statement,某些情况下会切换到Row格式。
注意:5.7.7之前的版本默认为 Statement Level,之后默认为 Row Level
mysql> show variables like 'binlog_format';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| binlog_format | ROW |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
数据的解析就是将二进制 binlog 格式,解析成 sql 语句的形式。
因为手边没有 Linux 环境,将在 mac 环境下整理以下操作,mac 环境下默认应该没有开启 binlog,我们先进行一些配置
确认是否开启 binlog
mysql> show variables like 'log_bin';
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| log_bin | OFF |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
可以看到显示 OFF
通过修改 my.cnf 文件使其支持,先查看文件位置
AlfreddeMacBook-Pro:etc alfred$ mysql --help --verbose | grep my.cnf
order of preference, my.cnf, $MYSQL_TCP_PORT,
/etc/my.cnf /etc/mysql/my.cnf /usr/local/mysql/etc/my.cnf ~/.my.cnf
AlfreddeMacBook-Pro:etc alfred$
注意:安装包默认没有开启使用binlog,且mac安装默认没有
my.cnf文件,需要自己在/etc目录下新建文件并添加相应配置
在/etc 新建文件my.cnf并添加如下内容
[mysqld]
#log_bin
log-bin = mysql-bin #开启binlog
binlog-format = ROW #选择row模式
server_id = 1 #配置mysql replication需要定义,不能和canal的slaveId重复
重启mysql服务,再次查看是否生效
mysql> show variables like "log_bin";
+---------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+---------------+-------+
| log_bin | ON |
+---------------+-------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
mysql>
我们先来建一些基础数据
建立一张表 t1,包含两个字段 id 和 name
mysql> CREATE TABLE t1 (id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
mysql>
mysql> show tables;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| t1 |
+----------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
插入两行数据 name 字段值为 chenjingchao1 和 chenjingchao2
mysql> insert into t1(name) values('chenjingchao1'),('chenjingchao2');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.01 sec)
Records: 2 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> select * from t1;
+----+---------------+
| id | name |
+----+---------------+
| 1 | chenjingchao1 |
| 2 | chenjingchao2 |
+----+---------------+
2 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
根据时间点找到包含上面操作的binlog日志
先找到 mac 环境下 mysql 的日志目录
mysql> show variables like 'log_%';
+----------------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+----------------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
| log_bin | ON |
| log_bin_basename | /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin |
| log_bin_index | /usr/local/mysql/data/mysql-bin.index |
| log_bin_trust_function_creators | OFF |
| log_bin_use_v1_row_events | OFF |
| log_builtin_as_identified_by_password | OFF |
| log_error | /usr/local/mysql/data/mysqld.local.err |
| log_error_verbosity | 3 |
| log_output | FILE |
| log_queries_not_using_indexes | OFF |
| log_slave_updates | OFF |
| log_slow_admin_statements | OFF |
| log_slow_slave_statements | OFF |
| log_syslog | OFF |
| log_syslog_facility | daemon |
| log_syslog_include_pid | ON |
| log_syslog_tag | |
| log_throttle_queries_not_using_indexes | 0 |
| log_timestamps | UTC |
| log_warnings | 2 |
+----------------------------------------+----------------------------------------+
20 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql>
可以看到未经配置时,默认日志是放在在了 /usr/local/mysql/data/ 下
进入到/usr/local/mysql/目录下,使用ls -all查看权限,发现 data 是只有 mysql 可以访问的,
我们先用sudo ls -l data查看一下 data 目录里是否有 binlog 日志,发现确实有如下二进制文件:
-rw-r----- 1 _mysql _mysql 911 Mar 16 23:20 mysql-bin.000001
我们可以利用 MySQL 自带的工具 mysqlbinlog 来进行解析,看看里面内容内容是否与我们写入的一致
AlfreddeMacBook-Pro:mysql alfred$ /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --base64-output=dec
ode-rows -v mysql-bin.000001
/*!50530 SET @@SESSION.PSEUDO_SLAVE_MODE=1*/;
/*!50003 SET @OLD_COMPLETION_TYPE=@@COMPLETION_TYPE,COMPLETION_TYPE=0*/;
DELIMITER /*!*/;
# at 4
#200316 21:27:17 server id 1 end_log_pos 123 CRC32 0xfdb649ac Start: binlog v 4, server v 5.7.10-log created 200316 21:27:17 at startup
# Warning: this binlog is either in use or was not closed properly.
ROLLBACK/*!*/;
# at 123
#200316 21:27:17 server id 1 end_log_pos 154 CRC32 0x5a6e0b99 Previous-GTIDs
# [empty]
# at 154
#200316 21:30:45 server id 1 end_log_pos 219 CRC32 0x3854f2b3 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=0 sequence_number=1
SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/;
# at 219
#200316 21:30:45 server id 1 end_log_pos 334 CRC32 0x2df34e5d Query thread_id=23 exec_time=0 error_code=0
use `test`/*!*/;
SET TIMESTAMP=1584365445/*!*/;
SET @@session.pseudo_thread_id=23/*!*/;
SET @@session.foreign_key_checks=1, @@session.sql_auto_is_null=0, @@session.unique_checks=1, @@session.autocommit=1/*!*/;
SET @@session.sql_mode=1436549152/*!*/;
SET @@session.auto_increment_increment=1, @@session.auto_increment_offset=1/*!*/;
/*!\C utf8 *//*!*/;
SET @@session.character_set_client=33,@@session.collation_connection=33,@@session.collation_server=8/*!*/;
SET @@session.lc_time_names=0/*!*/;
SET @@session.collation_database=DEFAULT/*!*/;
DROP TABLE `t1` /* generated by server */
/*!*/;
# at 334
#200316 23:19:50 server id 1 end_log_pos 399 CRC32 0x69490bae Anonymous_GTID last_committed=1 sequence_number=2
SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/;
# at 399
#200316 23:19:50 server id 1 end_log_pos 622 CRC32 0x57ec6aea Query thread_id=23 exec_time=0 error_code=0
SET TIMESTAMP=1584371990/*!*/;
CREATE TABLE t1 (id int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, name varchar(60) DEFAULT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (id)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
/*!*/;
# at 622
#200316 23:20:07 server id 1 end_log_pos 687 CRC32 0x99d4348b Anonymous_GTID last_committed=2 sequence_number=3
SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/;
# at 687
#200316 23:20:07 server id 1 end_log_pos 759 CRC32 0xd68e1831 Query thread_id=23 exec_time=0 error_code=0
SET TIMESTAMP=1584372007/*!*/;
BEGIN
/*!*/;
# at 759
#200316 23:20:07 server id 1 end_log_pos 807 CRC32 0x7b38f2b6 Table_map: `test`.`t1` mapped to number 109
# at 807
#200316 23:20:07 server id 1 end_log_pos 880 CRC32 0x56cf103e Write_rows: table id 109 flags: STMT_END_F
### INSERT INTO `test`.`t1`
### SET
### @1=1
### @2='chenjingchao1'
### INSERT INTO `test`.`t1`
### SET
### @1=2
### @2='chenjingchao2'
# at 880
#200316 23:20:07 server id 1 end_log_pos 911 CRC32 0x740f10e7 Xid = 18
COMMIT/*!*/;
SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'AUTOMATIC' /* added by mysqlbinlog */ /*!*/;
DELIMITER ;
# End of log file
/*!50003 SET COMPLETION_TYPE=@OLD_COMPLETION_TYPE*/;
/*!50530 SET @@SESSION.PSEUDO_SLAVE_MODE=0*/;
AlfreddeMacBook-Pro:mysql alfred$
可以看到解析出的 sql 与我们写入的一致,可以很方便地查看某人在数据中做了哪些修改。
所以对于一般 insert 误插入的数据,可以解析成反向 sql 语句 delete 后修改。但对于生产系统,如果 binlog 设置为 2GB,解析出的 SQL 会有成千万行,这个量级我们手动修改短时间是无法完成的,那么有没有一种可以直接生成反向 sql 语句的方式呢,答案是有的,介绍两种工具:
这是一个 perl 脚本
#!/usr/lib/perl -w
use strict;
use warnings;
use Class::Struct;
use Getopt::Long qw(:config no_ignore_case); # GetOption
# register handler system signals
use sigtrap 'handler', \&sig_int, 'normal-signals';
# catch signal
sub sig_int(){
my ($signals) = @_;
print STDERR "# Caught SIG$signals.\n";
exit 1;
}
my %opt;
my $srcfile;
my $host = '127.0.0.1';
my $port = 3306;
my ($user,$pwd);
my ($MYSQL, $MYSQLBINLOG, $ROLLBACK_DML);
my $outfile = '/dev/null';
my (%do_dbs,%do_tbs);
# tbname=>tbcol, tbcol: @n=>colname,type
my %tbcol_pos;
my $SPLITER_COL = ',';
my $SQLTYPE_IST = 'INSERT';
my $SQLTYPE_UPD = 'UPDATE';
my $SQLTYPE_DEL = 'DELETE';
my $SQLAREA_WHERE = 'WHERE';
my $SQLAREA_SET = 'SET';
my $PRE_FUNCT = '========================== ';
# =========================================================
# 基于row模式的binlog,生成DML(insert/update/delete)的rollback语句
# 通过mysqlbinlog -v 解析binlog生成可读的sql文件
# 提取需要处理的有效sql
# "### "开头的行.如果输入的start-position位于某个event group中间,则会导致"无法识别event"错误
#
# 将INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE 的sql反转,并且1个完整sql只能占1行
# INSERT: INSERT INTO => DELETE FROM, SET => WHERE
# UPDATE: WHERE => SET, SET => WHERE
# DELETE: DELETE FROM => INSERT INTO, WHERE => SET
# 用列名替换位置@{1,2,3}
# 通过desc table获得列顺序及对应的列名
# 特殊列类型value做特别处理
# 逆序
#
# 注意:
# 表结构与现在的表结构必须相同[谨记]
# 由于row模式是幂等的,并且恢复是一次性,所以只提取sql,不提取BEGIN/COMMIT
# 只能对INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE进行处理
# ========================================================
sub main{
# get input option
&get_options();
#
&init_tbcol();
#
&do_binlog_rollback();
}
&main();
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : get options and set option flag
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub get_options{
#Get options info
GetOptions(\%opt,
'help', # OUT : print help info
'f|srcfile=s', # IN : binlog file
'o|outfile=s', # out : output sql file
'h|host=s', # IN : host
'u|user=s', # IN : user
'p|password=s', # IN : password
'P|port=i', # IN : port
'start-datetime=s', # IN : start datetime
'stop-datetime=s', # IN : stop datetime
'start-position=i', # IN : start position
'stop-position=i', # IN : stop position
'd|database=s', # IN : database, split comma
'T|table=s', # IN : table, split comma
'i|ignore', # IN : ignore binlog check ddl and so on
'debug', # IN : print debug information
) or print_usage();
if (!scalar(%opt)) {
&print_usage();
}
# Handle for options
if ($opt{'f'}){
$srcfile = $opt{'f'};
}else{
&merror("please input binlog file");
}
$opt{'h'} and $host = $opt{'h'};
$opt{'u'} and $user = $opt{'u'};
$opt{'p'} and $pwd = $opt{'p'};
$opt{'P'} and $port = $opt{'P'};
if ($opt{'o'}) {
$outfile = $opt{'o'};
# 清空 outfile
`echo '' > $outfile`;
}
#
$MYSQL = qq{mysql -h$host -u$user -p'$pwd' -P$port};
&mdebug("get_options::MYSQL\n\t$MYSQL");
# 提取binlog,不需要显示列定义信息,用-v,而不用-vv
$MYSQLBINLOG = qq{mysqlbinlog -v};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --start-position=".$opt{'start-position'} if $opt{'start-position'};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --stop-position=".$opt{'stop-position'} if $opt{'stop-postion'};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --start-datetime='".$opt{'start-datetime'}."'" if $opt{'start-datetime'};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " --stop-datetime='$opt{'stop-datetime'}'" if $opt{'stop-datetime'};
$MYSQLBINLOG .= " $srcfile";
&mdebug("get_options::MYSQLBINLOG\n\t$MYSQLBINLOG");
# 检查binlog中是否含有 ddl sql: CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME
&check_binlog() unless ($opt{'i'});
# 不使用mysqlbinlog过滤,USE dbname;方式可能会漏掉某些sql,所以不在mysqlbinlog过滤
# 指定数据库
if ($opt{'d'}){
my @dbs = split(/,/,$opt{'d'});
foreach my $db (@dbs){
$do_dbs{$db}=1;
}
}
# 指定表
if ($opt{'T'}){
my @tbs = split(/,/,$opt{'T'});
foreach my $tb (@tbs){
$do_tbs{$tb}=1;
}
}
# 提取有效DML SQL
$ROLLBACK_DML = $MYSQLBINLOG." | grep '^### '";
# 去掉注释: '### ' -> ''
# 删除首尾空格
$ROLLBACK_DML .= " | sed 's/###\\s*//g;s/\\s*\$//g'";
&mdebug("rollback dml\n\t$ROLLBACK_DML");
# 检查内容是否为空
my $cmd = "$ROLLBACK_DML | wc -l";
&mdebug("check contain dml sql\n\t$cmd");
my $size = `$cmd`;
chomp($size);
unless ($size >0){
&merror("binlog DML is empty:$ROLLBACK_DML");
};
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : check binlog contain DDL
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub check_binlog{
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT check_binlog");
my $cmd = "$MYSQLBINLOG ";
$cmd .= " | grep -E -i '^(CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME)' ";
&mdebug("check binlog has DDL cmd\n\t$cmd");
my $ddlcnt = `$cmd`;
chomp($ddlcnt);
my $ddlnum = `$cmd | wc -l`;
chomp($ddlnum);
my $res = 0;
if ($ddlnum>0){
# 在ddl sql前面加上前缀<DDL>
$ddlcnt = `echo '$ddlcnt' | sed 's/^/<DDL>/g'`;
&merror("binlog contain $ddlnum DDL:$MYSQLBINLOG. ddl sql:\n$ddlcnt");
}
return $res;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : init all table column order
# if input --database --table params, only get set table column order
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub init_tbcol{
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT init_tbcol");
# 提取DML语句
my $cmd .= "$ROLLBACK_DML | grep -E '^(INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE)'";
# 提取表名,并去重
#$cmd .= " | awk '{if (\$1 ~ \"^UPDATE\") {print \$2}else {print \$3}}' | uniq ";
$cmd .= " | awk '{if (\$1 ~ \"^UPDATE\") {print \$2}else {print \$3}}' | sort | uniq ";
&mdebug("get table name cmd\n\t$cmd");
open ALLTABLE, "$cmd | " or die "can't open file:$cmd\n";
while (my $tbname = <ALLTABLE>){
chomp($tbname);
#if (exists $tbcol_pos{$tbname}){
# next;
#}
&init_one_tbcol($tbname) unless (&ignore_tb($tbname));
}
close ALLTABLE or die "can't close file:$cmd\n";
# init tb col
foreach my $tb (keys %tbcol_pos){
&mdebug("tbname->$tb");
my %colpos = %{$tbcol_pos{$tb}};
foreach my $pos (keys %colpos){
my $col = $colpos{$pos};
my ($cname,$ctype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/, $col);
&mdebug("\tpos->$pos,cname->$cname,ctype->$ctype");
}
}
};
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : init one table column order
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub init_one_tbcol{
my $tbname = shift;
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT init_one_tbcol");
# 获取表结构及列顺序
my $cmd = $MYSQL." --skip-column-names --silent -e 'desc $tbname'";
# 提取列名,并拼接
$cmd .= " | awk -F\'\\t\' \'{print NR\"$SPLITER_COL`\"\$1\"`$SPLITER_COL\"\$2}'";
&mdebug("get table column infor cmd\n\t$cmd");
open TBCOL,"$cmd | " or die "can't open desc $tbname;";
my %colpos;
while (my $line = <TBCOL>){
chomp($line);
my ($pos,$col,$coltype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/,$line);
&mdebug("linesss=$line\n\t\tpos=$pos\n\t\tcol=$col\n\t\ttype=$coltype");
$colpos{$pos} = $col.$SPLITER_COL.$coltype;
}
close TBCOL or die "can't colse desc $tbname";
$tbcol_pos{$tbname} = \%colpos;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : rollback sql: INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub do_binlog_rollback{
my $binlogfile = "$ROLLBACK_DML ";
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT do_binlog_rollback");
# INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE
my $sqltype;
# WHERE|SET
my $sqlarea;
my ($tbname, $sqlstr) = ('', '');
my ($notignore, $isareabegin) = (0,0);
# output sql file
open SQLFILE, ">> $outfile" or die "Can't open sql file:$outfile";
# binlog file
open BINLOG, "$binlogfile |" or die "Can't open file: $binlogfile";
while (my $line = <BINLOG>){
chomp($line);
if ($line =~ /^(INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE)/){
# export sql
if ($sqlstr ne ''){
$sqlstr .= ";\n";
print SQLFILE $sqlstr;
&mdebug("export sql\n\t".$sqlstr);
$sqlstr = '';
}
if ($line =~ /^INSERT/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_IST;
$tbname = `echo '$line' | awk '{print \$3}'`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{DELETE FROM $tbname};
}elsif ($line =~ /^UPDATE/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_UPD;
$tbname = `echo '$line' | awk '{print \$2}'`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{UPDATE $tbname};
}elsif ($line =~ /^DELETE/){
$sqltype = $SQLTYPE_DEL;
$tbname = `echo '$line' | awk '{print \$3}'`;
chomp($tbname);
$sqlstr = qq{INSERT INTO $tbname};
}
# check ignore table
if(&ignore_tb($tbname)){
$notignore = 0;
&mdebug("<BINLOG>#IGNORE#:line:".$line);
$sqlstr = '';
}else{
$notignore = 1;
&mdebug("<BINLOG>#DO#:line:".$line);
}
}else {
if($notignore){
&merror("can't get tbname") unless (defined($tbname));
if ($line =~ /^WHERE/){
$sqlarea = $SQLAREA_WHERE;
$sqlstr .= qq{ SET};
$isareabegin = 1;
}elsif ($line =~ /^SET/){
$sqlarea = $SQLAREA_SET;
$sqlstr .= qq{ WHERE};
$isareabegin = 1;
}elsif ($line =~ /^\@/){
$sqlstr .= &deal_col_value($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line);
$isareabegin = 0;
}else{
&mdebug("::unknown sql:".$line);
}
}
}
}
# export last sql
if ($sqlstr ne ''){
$sqlstr .= ";\n";
print SQLFILE $sqlstr;
&mdebug("export sql\n\t".$sqlstr);
}
close BINLOG or die "Can't close binlog file: $binlogfile";
close SQLFILE or die "Can't close out sql file: $outfile";
# 逆序
# 1!G: 只有第一行不执行G, 将hold space中的内容append回到pattern space
# h: 将pattern space 拷贝到hold space
# $!d: 除最后一行都删除
my $invert = "sed -i '1!G;h;\$!d' $outfile";
my $res = `$invert`;
&mdebug("inverter order sqlfile :$invert");
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : transfer column pos to name
# deal column value
#
# &deal_col_value($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line);
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub deal_col_value($$$$$){
my ($tbname, $sqltype, $sqlarea, $isareabegin, $line) = @_;
&mdebug("$PRE_FUNCT deal_col_value");
&mdebug("input:tbname->$tbname,type->$sqltype,area->$sqlarea,areabegin->$isareabegin,line->$line");
my @vals = split(/=/, $line);
my $pos = substr($vals[0],1);
my $valstartpos = length($pos)+2;
my $val = substr($line,$valstartpos);
my %tbcol = %{$tbcol_pos{$tbname}};
my ($cname,$ctype) = split(/$SPLITER_COL/,$tbcol{$pos});
&merror("can't get $tbname column $cname type") unless (defined($cname) || defined($ctype));
&mdebug("column infor:cname->$cname,type->$ctype");
# join str
my $joinstr;
if ($isareabegin){
$joinstr = ' ';
}else{
# WHERE 被替换为 SET, 使用 , 连接
if ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_WHERE){
$joinstr = ', ';
# SET 被替换为 WHERE 使用 AND 连接
}elsif ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_SET){
$joinstr = ' AND ';
}else{
&merror("!!!!!!The scripts error");
}
}
#
my $newline = $joinstr;
# NULL value
if (($val eq 'NULL') && ($sqlarea eq $SQLAREA_SET)){
$newline .= qq{ $cname IS NULL};
}else{
# timestamp: record seconds
if ($ctype eq 'timestamp'){
$newline .= qq{$cname=from_unixtime($val)};
# datetime: @n=yyyy-mm-dd hh::ii::ss
}elsif ($ctype eq 'datetime'){
$newline .= qq{$cname='$val'};
}else{
$newline .= qq{$cname=$val};
}
}
&mdebug("\told>$line\n\tnew>$newline");
return $newline;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : check is ignore table
# params: IN table full name # format:`dbname`.`tbname`
# RETURN:
# 0 not ignore
# 1 ignore
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub ignore_tb($){
my $fullname = shift;
# 删除`
$fullname =~ s/`//g;
my ($dbname,$tbname) = split(/\./,$fullname);
my $res = 0;
# 指定了数据库
if ($opt{'d'}){
# 与指定库相同
if ($do_dbs{$dbname}){
# 指定表
if ($opt{'T'}){
# 与指定表不同
unless ($do_tbs{$tbname}){
$res = 1;
}
}
# 与指定库不同
}else{
$res = 1;
}
}
#&mdebug("Table check ignore:$fullname->$res");
return $res;
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print debug msg
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub mdebug{
my (@msg) = @_;
print "<DEBUG>@msg\n" if ($opt{'debug'});
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print error msg and exit
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub merror{
my (@msg) = @_;
print "<Error>:@msg\n";
&print_usage();
exit(1);
}
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Func : print usage
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
sub print_usage{
print <<EOF;
==========================================================================================
Command line options :
--help # OUT : print help info
-f, --srcfile # IN : binlog file. [required]
-o, --outfile # OUT : output sql file. [required]
-h, --host # IN : host. default '127.0.0.1'
-u, --user # IN : user. [required]
-p, --password # IN : password. [required]
-P, --port # IN : port. default '3306'
--start-datetime # IN : start datetime
--stop-datetime # IN : stop datetime
--start-position # IN : start position
--stop-position # IN : stop position
-d, --database # IN : database, split comma
-T, --table # IN : table, split comma. [required] set -d
-i, --ignore # IN : ignore binlog check contain DDL(CREATE|ALTER|DROP|RENAME)
--debug # IN : print debug information
Sample :
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd'
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' -i
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' --debug
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -h '192.168.1.2' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' -P 3307
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' --start-position=107
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' --start-position=107 --stop-position=10000
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.000001' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' -d 'db1,db2'
shell> perl binlog-rollback.pl -f 'mysql-bin.0000*' -o '/tmp/t.sql' -u 'user' -p 'pwd' -d 'db1,db2' -T 'tb1,tb2'
==========================================================================================
EOF
exit;
}
1;
使用该工具生成反向 sql ,可以基于位置点和基于时间点的恢复,使用格式和 sample 也写的非常详细
由美团开源的代码
与binlog-rollback不同的是:不需要输入用户名密码;生成的binlog_output_base.flashback是反解后的二进制文件,生成这个文件进行恢复的好处是要比binlog-rollback工具生成sql语句的方式要快很多
操作此处略过
如果觉得binlog恢复比较慢,可以引入这个延迟从库的架构
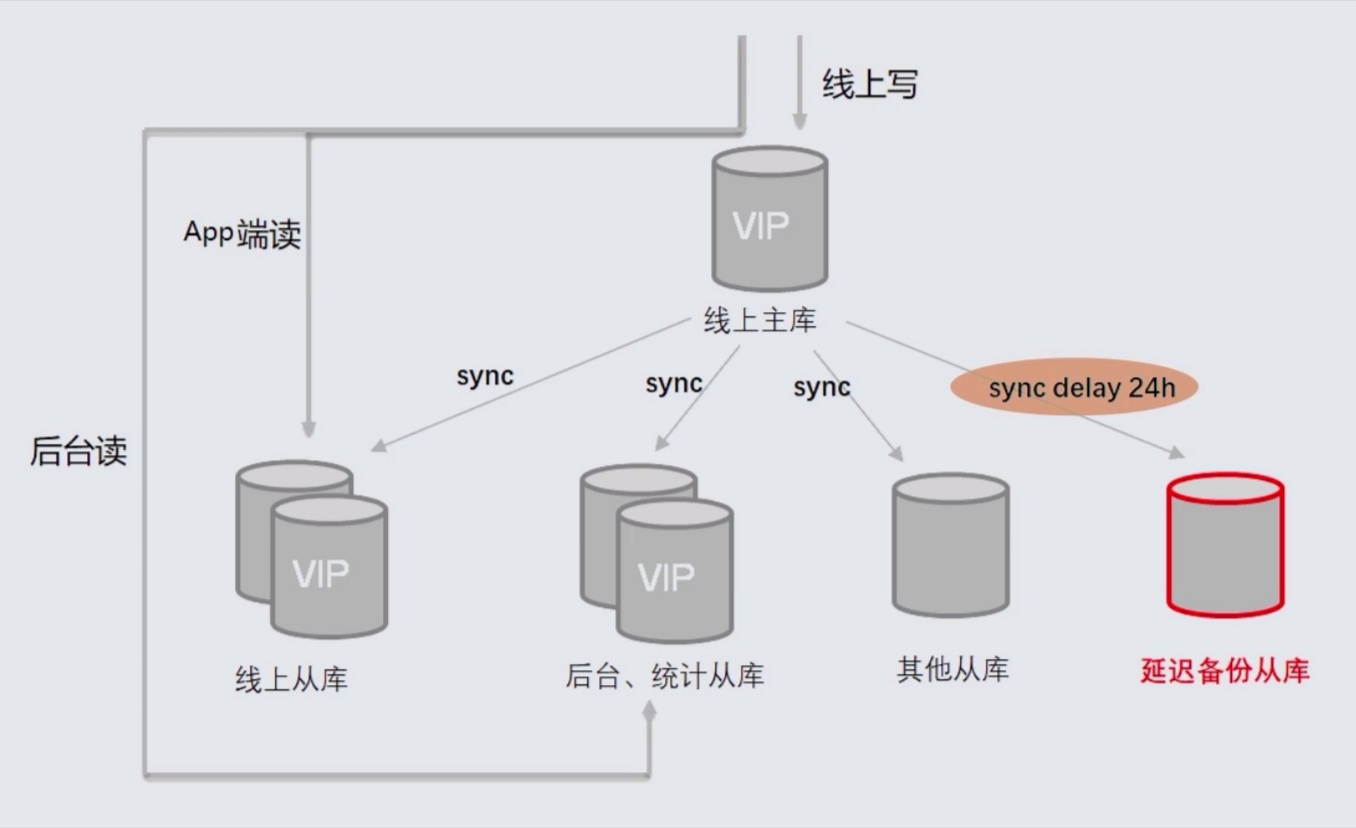
增加一个从库(延迟备份从库),对它进行延迟处理,比如当有人误操作了,DBA在24小时内可以登录使用这个从库进行数据恢复。